Volte Call Drop
One of the most important KPI is the LTE Call Drop Rate. Every network is striving to improve this KPI and it has become more important in LTE since the introduction of VoLTE. In simple words, a call drop in LTE means that a user’s ongoing session is dropped requiring the user to initiate a new connection to resume services. At the eNB level, this can be seen as an abnormal release which is verified from the cause code inside the Context Release message.
Common Causes for Call Drops
Like other KPIs, the call drop is also divided into two broad categories
• Radio Induced Drops
• MME Induced Drops
1. Radio Induced Call Drops
DL RLC Retransmissions
The most common drop pegged under Radio issues is the drop due to RLC retransmissions. If a network has a maximum of 16 RLC retransmissions for downlink, the eNB will send a message 16 times at the RLC layer and if the UE is unable to decode it or send an acknowledgement, the eNB will consider this a RLF. Some vendor initiate a UE Context Release at this point resulting in a abnormal release and a call drop. Some vendors wait for a bit longer (internal timer - implementation specific)for the UE to initiate RRC Reestablishment and if there is no Reestablishment then eNB will release abnormally and radio induced call drop will be pegged.

Optimization
The most common issue for this kind of failure is when the target cell is very far away such that when the UE initiates handover on the target cell, it is at a distance beyond the cell radius. So, the target cell fails to decode the dedicated RACH properly for this UE and it results in a handover failure. So, in this case, either increase the cell radius of the target cell or down tilt it so that it does not overshoot beyond its planned radius. This can also happen in areas where there are large water bodies as signals easily tend to get reflected over water. In such cases, either forbid handovers to such cells or add offsets for those cells to make handovers difficult.
Drop Due to No Response
If an eNB sends a signalling message for instance RRC Reconfiguration then it expects a response from the UE. If the UE does not send a RRC Reconfiguration Complete message to the eNB and the internal timer on the eNB expires, then the eNB initiates a release. This timer is usually a large value, so such a drop is rare. If such drops are seen then verify that the eNB’s internal timer is not set to a very small value.
Point to note is that RRC Reconfiguration for mobility command is excluded from this mechanism as the UE needs to send its response to the target cell and not to the source cell.
Other Optimization Work Around
The value of UE Inactivity timer also plays an important part in the calculation of Call Drop Rate. The expiry of this timer means that the UE has been inactive for some time and the eNB releases it. The UE goes to idle mode and the eNB pegs a normal release. The Call Drop Rate is ratio of total abnormal releases to the total normal releases. So, if the UE Inactivity timer is a small value, there will be a greater number of normal releases which can artificially reduce the CDR. In short, while benchmarking two different networks, it is important to verify that they have the same UE Inactivity Timer value so that they can be compared properly.
However, reducing the inactivity timer can cause an increase in RRC signalling so it should not be reduced excessively.
2. MME Induced Drops
The MME drops are usually caused by radio issues but they are pegged under MME drops because the eNB has no way of knowing that the drop was caused by a radio issue. Lets understand with help of different cases that are pegged under MME induced drops.
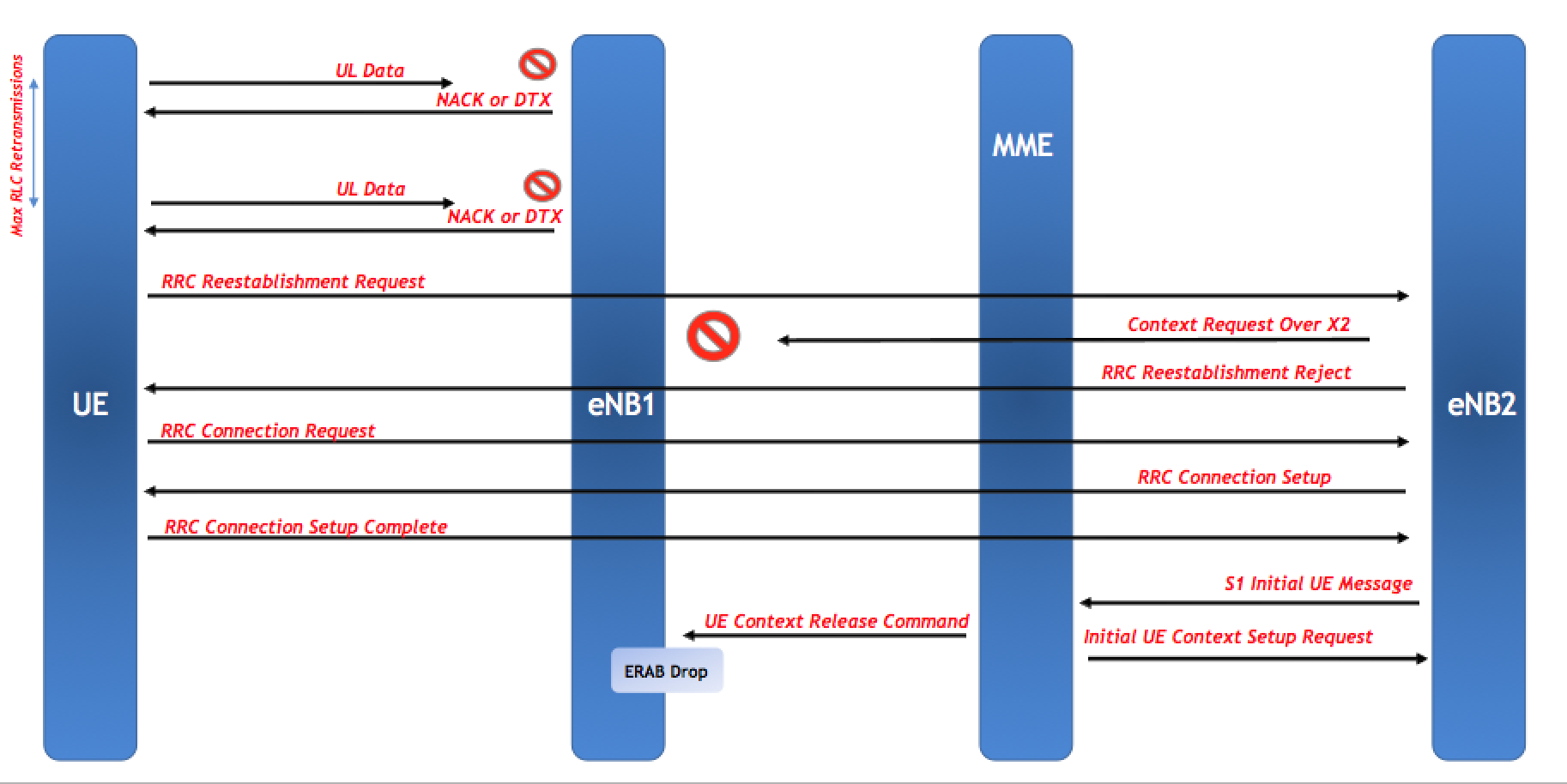
Uplink RLC Retransmission Issue
Consider a UE that experienced RLF due to maximum number of uplink RLC retransmission. Such a UE will initiate a RRC ReEstablishment procedure to regain its radio link. Now this RRC ReEstablishment can be to the serving cell and in that case, it is usually successful since the serving cell already has the UE’s context. However, this RRC ReEstablishment can also be sent to another cell from eNB2 that does not belong to the source eNB (eNB1). In this case, if eNB2 is a neighbor of the eNB1 so it will try to fetch the context for this UE from eNB1 and based on that it will accept the RRC ReEstablishment. However, if the eNB2 is not a neighbour then it will reject the RRC ReEstablishment. From the UE’s perspective this will be considered a call drop but at the eNB1, the eNB still does not know that this UE has experienced RLF. Now, the UE will initiate a new RRC Connection at the eNB2 and based on that the eNB2 will forward S1 Initial UE Message to the MME. MME will check the UE and it will find out that this UE’s context already exists on the eNB1 so it will send a UE Context Release to the eNB1 and then it will send S1 Initial Context Setup Request to the eNB2. The eNB1 will consider this a MME induced drop since the eNB1 still holds the UE’s context and a release from MME is considered abnormal. However, in reality, such a release is caused by a failure over the radio interface but the eNB1 does not have this knowledge.
- Optimization
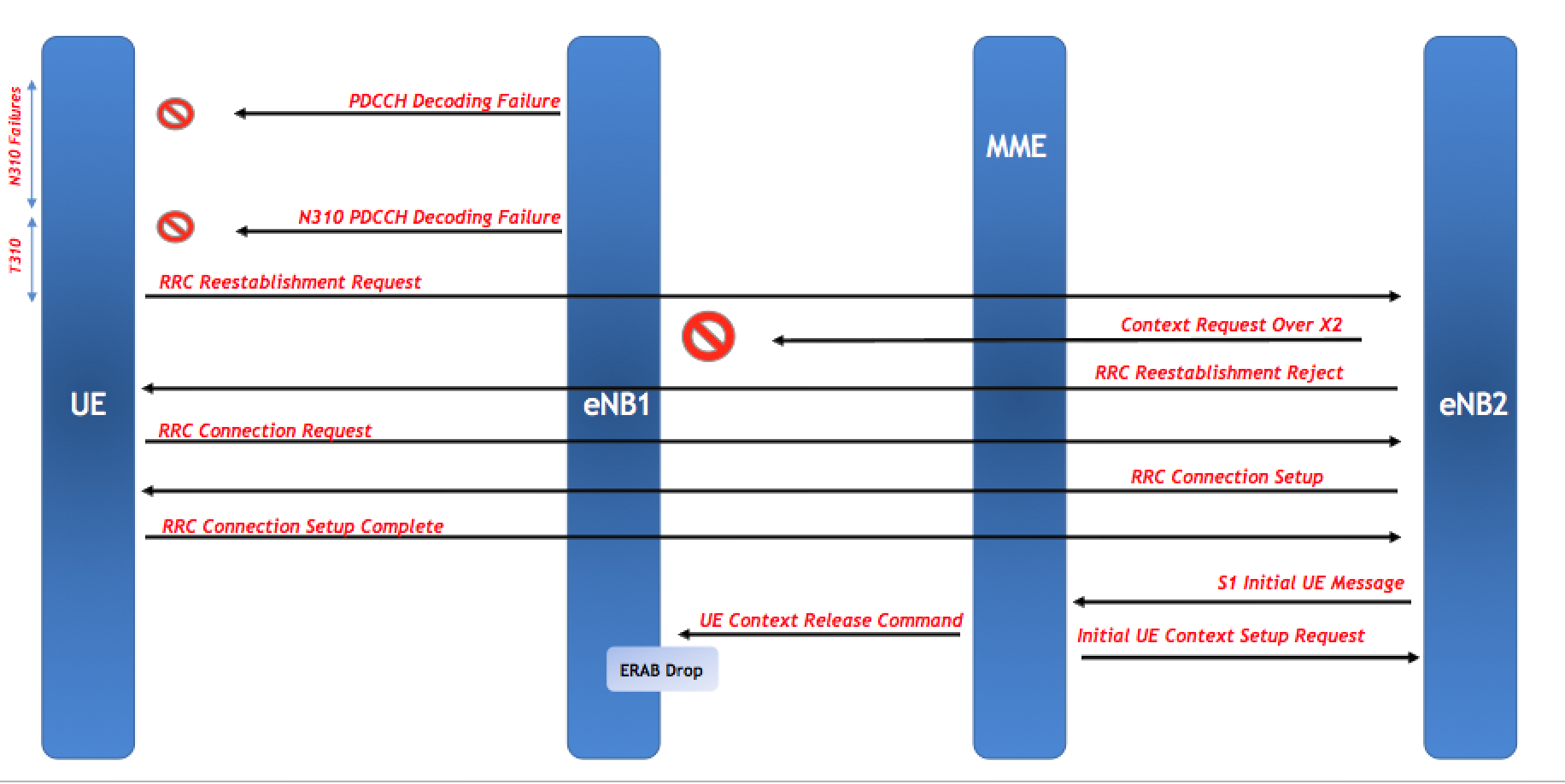
N310 PDCCH Decoding Failures
If the UE is unable to decode PDCCH in DL for N310 consecutive intervals, the UE will initiate a RRC ReEstablishment. N310 indicates an interval of 200 consecutive PDCCH decoding failures. Simply put, if the UE fails to decode PDCCH for 200ms, it will be considered one N310. If the N310 value is 2 then it means that if the UE fails to decode PDCCH for 400 ms, it will have exceeded the configured N310 threshold. Once, N310 has been exceeded, the UE starts timer T310 and if the UE is unable to retain the connection (still unable to decode PDCCH) before T310 expires, the UE will initiate RRC ReEstablishment. Let’s understand with an example. Consider N310 of 2 and T310 of 500ms, then the UE will initiate RRC Connection ReEstablishment after 900 ms (N310 = 400ms + T310 = 500ms).
Again, in this case, if the UE receives a RRC ReEstablishment Rejection from the eNB2, then the UE will initiate a new RRC Connection. Once the RRC Connection is setup, the eNB2 will send a S1 Initial UE Message to the MME and consequently, MME will send a UE Context Release Command to the eNB1 since MME already has the context of this UE against eNB1 and in order to process Initial Context Setup on eNB2, it has to release the context on eNB1.
- Optimization
Handover Drop Due To MME
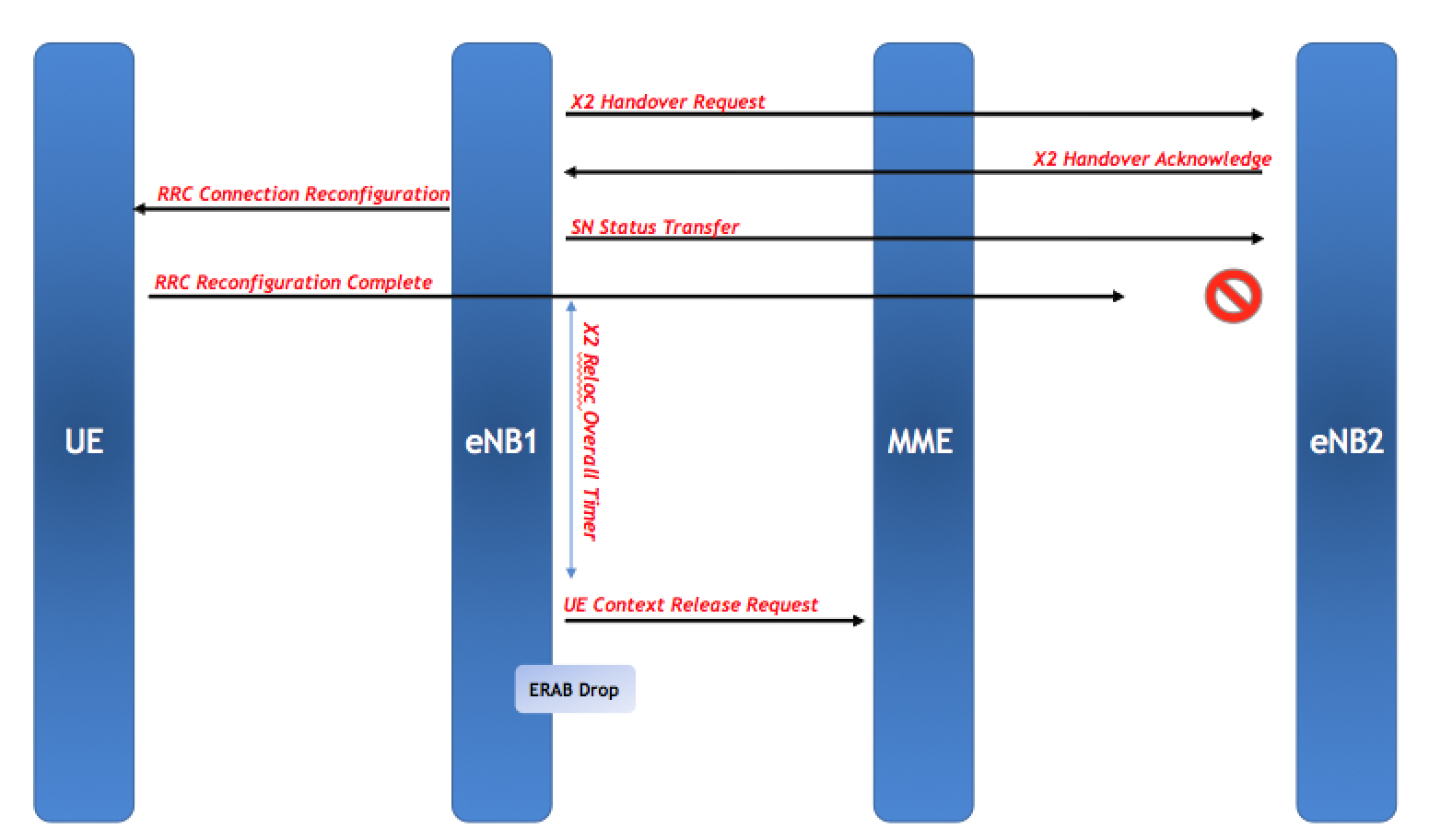
Another drop that is pegged under MME is the handover induced drop. As described before, the HO failure induced drop is pegged under radio due to X2 Reloc Overall Timer expiry. However, if the UE fails the handover then it tries RRC ReEstablishment after T304 expires and if that also fails then the UE will try a new RRC Connection. Once again, the new eNB will send a S1 Initial UE Message to the MME and MME will send a UE Context Release to the source eNB resulting in a Handover Drop due to MME. The main difference between handover failure pegged in radio and MME is the time the UE takes to initiate the new RRC Connection. If the UE initiates a new RRC connection before the source eNB’s X2 Reloc Overall Timer expiry then it will be pegged under MME drop while if the UE is unable to initiate a new RRC Connection in time, the source eNB will release the context due to X2 Reloc Overall Timer expiry resulting in a radio drop.
Moreover, such an issue is usually observed when the UE tries RRC ReEstablishment on a third eNB which was not the target. It can also happen if the Inter-RAT handover fails and the UE retries RRC ReEstablishment on another eNB.
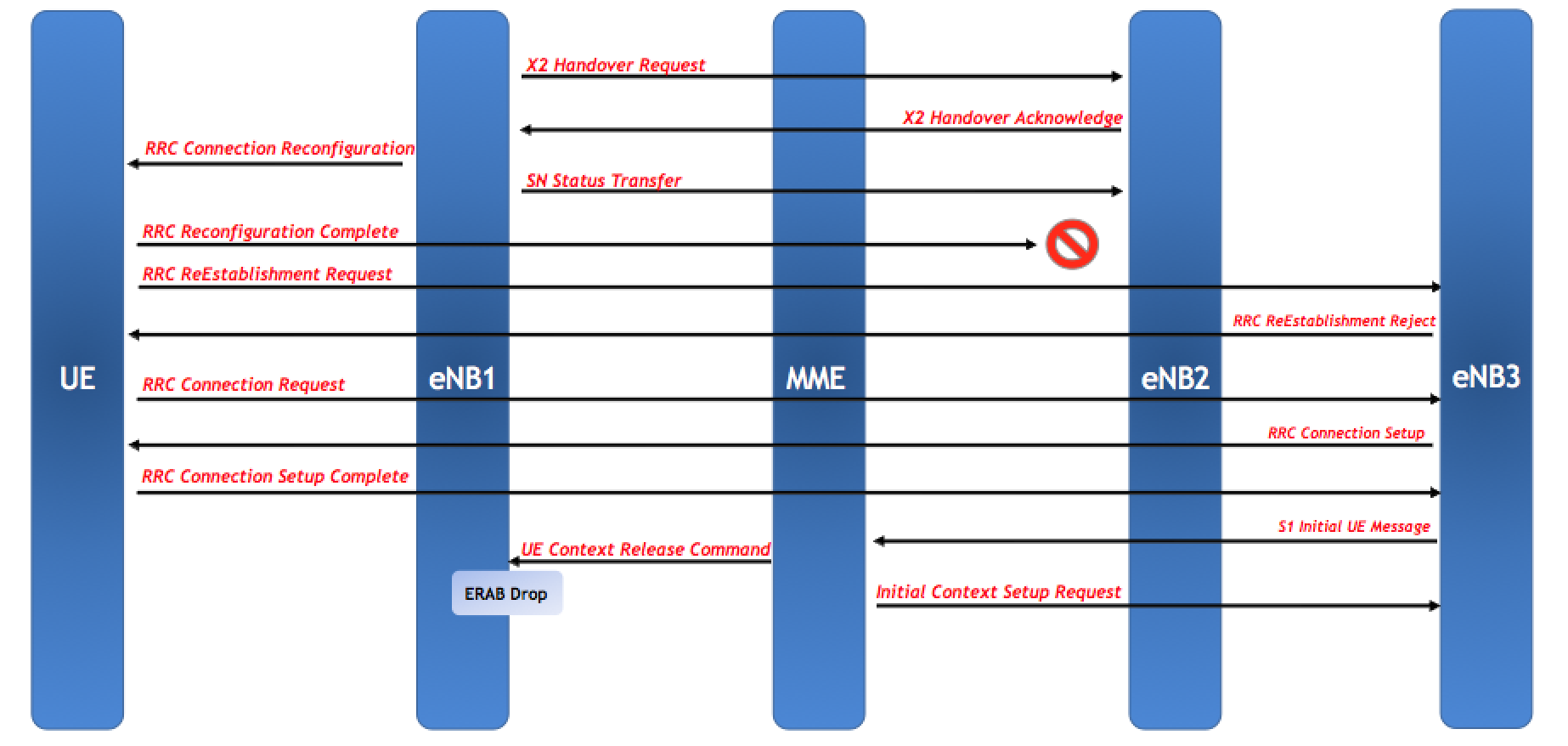
The point to understand is that in this case, the eNB is expecting a UE Context Release from the target eNB over X2. So, if it gets a UE Context Release Command from the MME, the eNB will consider this abnormal and it will peg it under MME drop.
- Optimization
Also, optimization of neighbors and verifying that functional X2 links are present for all the neighbors can greatly reduce the RRC ReEstablishment rejections since most of these rejections are caused due to absence of X2 links. Increasing the timer T301 can also reduce RRC ReEstablishment failures but it can also increase the delay from UE’s perspective, so it should not be increased excessively.
In case of any queries or feedback, please drop a comment below and I would love to respond and help.
Comments
Post a Comment